5 Signs You May Be Living With PTSD
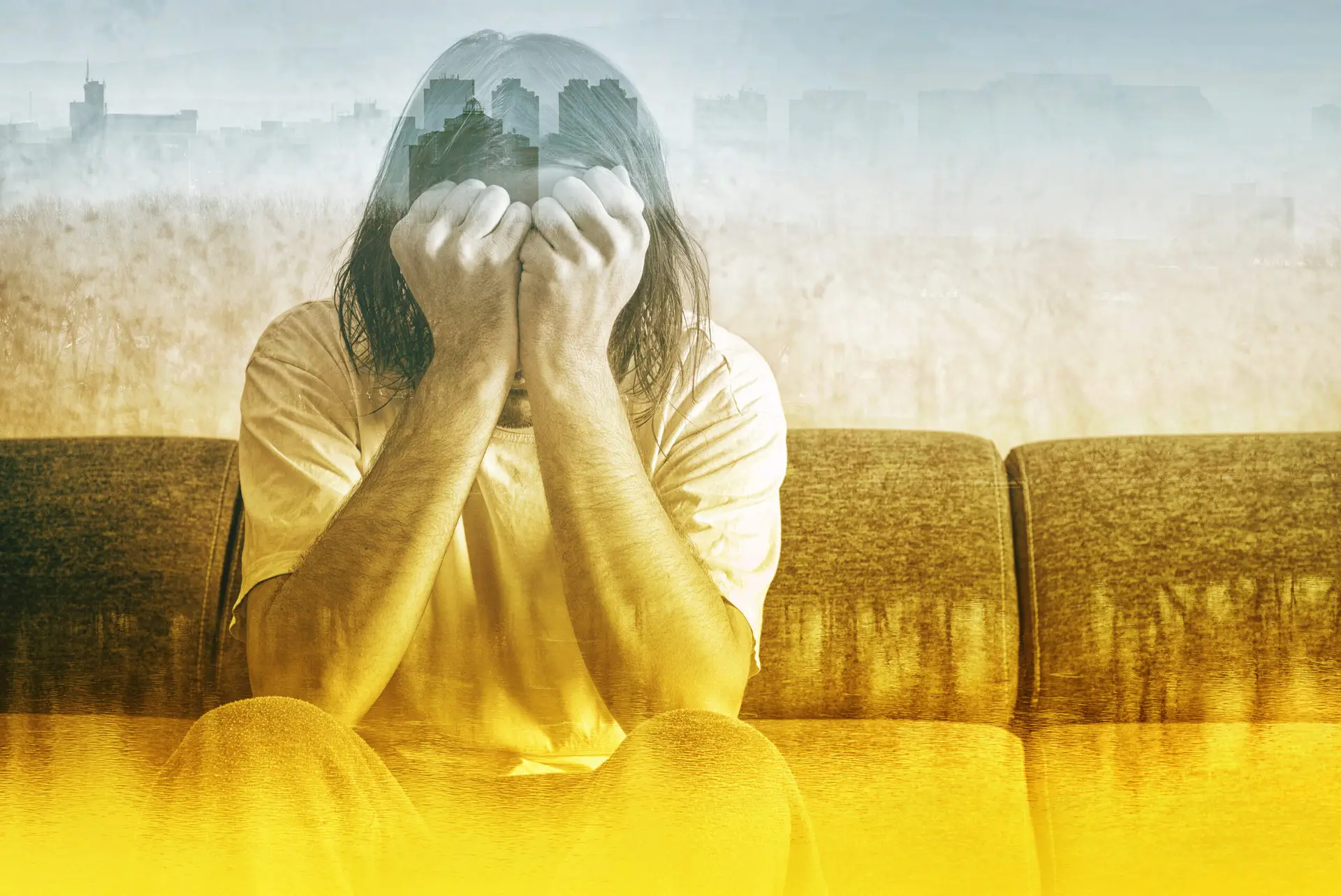
Do I have PTSD? That is a question you may be asking if you are experiencing flashbacks, nightmares, and intense fear or anxiety. Experiencing these symptoms could be signs of PTSD, or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Living with PTSD can be incredibly challenging, as the symptoms can disrupt daily life and lead to feelings of isolation and distress. In this article, we will explore five key signs that may indicate you are living with PTSD.
Recognizing the signs of PTSD is crucial for seeking appropriate help and support. By understanding these signs, you can gain insight into your own experiences and take steps towards healing and recovery. Whether you’ve endured a traumatic event recently or in the past, identifying these symptoms early on is essential for your mental health and well-being.
From recurring nightmares to hypervigilance and avoiding reminders of the trauma, each sign serves as a vital clue in uncovering the presence of PTSD. By understanding and addressing these signs, you can take control of your life again and embark on a journey of healing. Join us as we explore five signs that you may be living with PTSD and discover the resources available to help you navigate this difficult journey.
Understanding PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. These events can include natural disasters, physical or sexual assault, accidents, combat, or any other situation that evokes intense fear, helplessness, or horror. When someone experiences a traumatic event, it can have a profound impact on their psychological and emotional well-being, leading to a range of debilitating symptoms that can significantly disrupt their daily life.
PTSD is characterized by the brain’s inability to properly process and integrate the traumatic experience, resulting in the persistent re-experiencing of the event through intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares. Individuals with PTSD may also experience heightened arousal, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, and negative changes in their thoughts and mood. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, making it crucial for individuals to recognize the signs and seek professional help.
Understanding the nature of PTSD is the first step in addressing this condition. By recognizing the underlying causes, common symptoms, and the impact it can have on an individual’s life, we can better understand the challenges faced by those living with PTSD and provide them with the necessary support and resources to facilitate their recovery.

Common symptoms of PTSD
The symptoms of PTSD can vary widely from person to person, but there are several common experiences that individuals with this condition often share. These symptoms can be broadly divided into four main categories: re-experiencing, avoidance, negative changes in thoughts and mood, and hyperarousal.
Re-experiencing the traumatic event is a hallmark of PTSD, and can manifest through intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares. Individuals may feel as though they are reliving the trauma, with vivid sensory experiences that can be overwhelming and disruptive. Avoidance is another key symptom, as those with PTSD may go to great lengths to steer clear of reminders of the traumatic event, including places, people, or even their own thoughts and feelings about the experience.
Negative changes in thoughts and mood are also common, with individuals experiencing persistent feelings of guilt, shame, or detachment from others. They may have difficulty experiencing positive emotions or feel a sense of hopelessness about the future. Hyperarousal, characterized by increased physiological and emotional reactivity, can also be a significant challenge, leading to difficulties with sleep, concentration, and emotional regulation.
By understanding these common symptoms, individuals can better recognize the signs of PTSD and seek the appropriate support and treatment to address their unique experiences and facilitate their recovery.

Physical signs of PTSD
In addition to the emotional and psychological symptoms of PTSD, individuals may also experience a range of physical manifestations of the condition. These physical signs can be just as debilitating as the mental and emotional symptoms, and can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being.
One of the most common physical signs of PTSD is heightened physiological arousal, which can manifest as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and muscle tension. This heightened state of arousal can be triggered by reminders of the traumatic event, leading to a sense of panic or fear. Individuals may also experience headaches, gastrointestinal issues, and chronic pain, as the body’s stress response takes a toll on the physical systems. In another blog post we dove into 10 signs your pain may be trauma based.
Sleep disturbances are another prevalent physical sign of PTSD, with individuals struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep due to recurring nightmares or a general sense of hypervigilance. This lack of quality sleep can exacerbate other physical symptoms and contribute to overall feelings of fatigue and exhaustion.
Recognizing these physical signs of PTSD is crucial, as they can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily functioning and overall quality of life. By addressing the physical manifestations of the condition, individuals can take a more holistic approach to their recovery and improve their overall well-being.
Emotional signs of PTSD
The emotional impact of PTSD can be profound and far-reaching, affecting an individual’s ability to regulate their emotions, maintain healthy relationships, and engage in daily activities. Understanding the emotional signs of PTSD is essential for recognizing the condition and seeking appropriate support.
One of the most common emotional signs of PTSD is heightened anxiety and fear. Individuals may experience persistent feelings of dread, apprehension, and a sense of impending danger, even in the absence of any immediate threat. This can lead to a state of hypervigilance, where the individual is constantly on alert for potential threats, further exacerbating their emotional distress.
Feelings of guilt, shame, and worthlessness are also prevalent among individuals with PTSD. They may blame themselves for the traumatic event or feel that they should have been able to prevent it, leading to a deep sense of self-loathing and a belief that they are somehow undeserving of happiness or success. These negative emotions can be incredibly debilitating and can contribute to the development of depression or other mental health conditions.
Emotional numbing, or the inability to experience positive emotions, is another common sign of PTSD. Individuals may feel disconnected from their feelings, leading to a sense of detachment from their loved ones and the world around them. This emotional distance can further isolate the individual, making it challenging to seek support and engage in meaningful relationships.
Behavioural signs of PTSD
In addition to the physical and emotional symptoms of PTSD, individuals may also exhibit certain behavioral changes that can be indicative of the condition. These behavioral signs can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life and can affect their ability to maintain healthy relationships and engage in routine activities.
One of the most common behavioral signs of PTSD is avoidance. Individuals may go to great lengths to avoid any reminders of the traumatic event, including places, people, or activities that were once enjoyable. This avoidance can lead to a significant disruption in the individual’s daily routine and can further contribute to feelings of isolation and withdrawal.
Hypervigilance is another behavioral sign of PTSD, where individuals are constantly on the lookout for potential threats or danger. This heightened state of alertness can manifest in a variety of ways, such as constantly scanning the environment, startling easily, or feeling the need to be in control of their surroundings at all times. This hypervigilance can be incredibly draining and can make it difficult for individuals to relax or engage in activities that they once enjoyed.
Substance abuse is also a common behavioral sign of PTSD, as individuals may turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions and experiences associated with the condition. This coping mechanism can further exacerbate the symptoms of PTSD and can lead to the development of additional mental health and physical health issues.
PTSD risk factors
While anyone can develop PTSD after experiencing a traumatic event, certain risk factors can increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the condition. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals and healthcare providers identify those who may be at a higher risk and take proactive steps to address their mental health needs.
One of the primary risk factors for PTSD is the nature and severity of the traumatic event itself. Individuals who have experienced prolonged, repeated, or particularly horrific traumas, such as sexual assault, childhood abuse, or combat, are at a higher risk of developing PTSD. The more intense and overwhelming the traumatic experience, the greater the likelihood of developing the condition.
Genetic and biological factors can also play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to PTSD. Research has shown that individuals with certain genetic variations or neurological differences may be more prone to developing the condition, particularly in response to traumatic events. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression, may be at a higher risk of developing PTSD following a traumatic event.
Socioeconomic and demographic factors can also contribute to PTSD risk. Individuals from disadvantaged or marginalized communities, as well as those with limited access to mental health resources, may be more vulnerable to developing PTSD. Additionally, certain age groups, such as children and adolescents, may be more susceptible to the condition due to their stage of development and the unique challenges they face.
Seeking help for PTSD
Recognizing the signs of PTSD and seeking professional help is a crucial step in the journey towards healing and recovery. Ignoring or minimizing the symptoms can lead to further deterioration of mental and physical health, making it increasingly difficult to manage the condition and regain a sense of control over one’s life.
When seeking help for PTSD, it is important to find a mental health professional who specializes in trauma-informed care and has experience working with individuals with this condition. This may include therapists, counsellors, or psychologists who are trained in evidence-based treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR).
In addition to individual therapy, support groups can also be a valuable resource for individuals with PTSD. Connecting with others who have shared similar experiences can provide a sense of community, validation, and understanding that can be incredibly helpful in the recovery process. These support groups can be facilitated by mental health professionals or organized by community organizations.
It is also important to recognize that seeking help for PTSD may be a daunting and challenging process, as the symptoms of the condition can make it difficult to reach out and engage in treatment. Individuals may experience feelings of shame, fear, or mistrust, which can create barriers to accessing the support they need. However, with patience, compassion, and a commitment to their own well-being, individuals can overcome these obstacles and take the first steps towards healing.
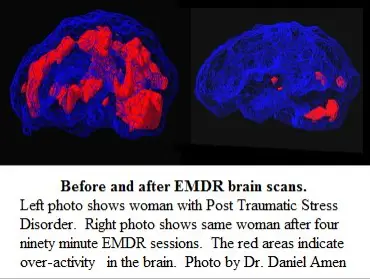
Treatment options for PTSD
Once an individual has sought professional help for PTSD, there are several evidence-based treatment options available to address the symptoms and facilitate the recovery process. The specific treatment approach will depend on the individual’s unique needs, the severity of their symptoms, and their personal preferences.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most widely recognized and effective treatments for PTSD. This approach focuses on identifying and challenging the negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to the individual’s distress, and challenging them with more adaptive and empowering perspectives. CBT can also involve exposure therapy, where the individual is gradually exposed to reminders of the traumatic event in a safe and controlled environment, helping to reduce the intensity of the associated fear and anxiety.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is an evidence-based treatment for PTSD, endorsed by leading health authorities around the world, which utilizes rapid eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to help the brain process and integrate the traumatic memories. This approach is designed to help the individual reprocess the traumatic event(s) in a way that neutralizes the emotional and physiological distress associated, and then updates the neurological and physiological networks with adaptive responses. Click here to read another of our popular blog posts on EMDR.
In addition to these psychological interventions, medication may also be a helpful component of PTSD treatment. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and sleep medications can be used to manage the symptoms of PTSD, such as intrusive thoughts, hyperarousal, and sleep disturbances. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication regimen and to monitor its effectiveness over time.
Coping strategies for living with PTSD
Living with PTSD can be a challenging and ongoing process, but there are a variety of coping strategies and self-care practices that can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. Incorporating these strategies into a comprehensive treatment plan can be a powerful tool in the journey towards healing and recovery.
One of the most important coping strategies for individuals with PTSD is to develop a strong support network. This may involve reaching out to trusted friends and family members, joining a support group, or engaging with a mental health professional on a regular basis. Having a safe and supportive environment can provide a sense of comfort and stability, which can be invaluable in the face of the challenges posed by PTSD.
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, can also be highly beneficial for individuals with PTSD. These practices can help to calm the mind, reduce physiological arousal, and promote a greater sense of emotional regulation. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or other forms of exercise, can help to alleviate the physical symptoms of PTSD and promote overall well-being.
It is also important for individuals with PTSD to be mindful of their self-care practices, such as maintaining a healthy sleep schedule, eating a nutritious diet, and finding ways to manage stress and reduce the risk of burnout. By prioritizing their own well-being, individuals with PTSD can build the resilience and resources they need to navigate the challenges of their condition and work towards a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Self-Assessment
While anyone suffering with emotional, psychological, or physical stress should always seek the help of a qualified professional, some find it useful to take a preliminary self-assessment before deciding it’s time to make a call.
Please note that while the following self-assessment tool may be helpful, it may also be triggering, and it cannot be used as a diagnostic tool. Only a formal diagnosis can be issued by the appropriate professional such as a Clinical Psychologist, or Psychiatrist.
https://www.healthyplace.com/psychological-tests/ptsd-test
Please be mindful of your wellbeing if you choose to self-assess. You may find other psychological assessments useful by visiting https://www.healthyplace.com/psychological-tests.
Conclusion
PTSD is a complex and multifaceted condition that can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical, emotional, and behavioral well-being. Understanding the signs and symptoms of PTSD is crucial for recognizing the condition and seeking the appropriate support and treatment.
From the intrusive thoughts and nightmares that characterize the re-experiencing of trauma to the avoidance and emotional numbing that can lead to social isolation, the signs of PTSD are varied and can manifest in a range of ways. By recognizing these physical, emotional, and behavioral indicators, individuals can take the first step towards addressing their condition and embarking on a journey of healing and recovery.
While the path to recovery may be challenging, there are a variety of evidence-based treatment options and coping strategies available to support individuals with PTSD. From cognitive-behavioral therapy and EMDR to medication and self-care practices, there are many tools and resources that can help individuals manage their symptoms and reclaim their sense of control and well-being.
By fostering a greater understanding of PTSD and the resources available for those living with the condition, we can work towards creating a more compassionate and supportive environment for those who have experienced trauma. Through education, advocacy, and a commitment to mental health, we can empower individuals with PTSD to overcome the challenges they face and embrace a future filled with hope and possibility.
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of the symptoms of PTSD, we can help. All clinicians at Grigore Counselling & Associates are experts in EMDR and use the latest evidence-based techniques such as Total Immersion EMDR to achieve clinically significant results in a fraction of the time compared to traditional approaches. Click here to schedule a free 45-minute consultation.











